- About Us
- Facilities
- Patient Stories
- Media & Events
- CSR
- Contact Us
- Book Appointment
Pune : 7411951943
Mumbai : 8123922650
Nashik : 7411804875
Kolhapur : 8147647685
Latur : 7411951965
Belagavi : 7411805024
Bengaluru : 7411951962
Mysore : 8971928968
Hyderabad : 8123919853
Secunderabad : 8123919853
Surat : 8147647677
Ludhiana : 7411951963
Gurugram : 8792498991
Kalaburagi : 9164045999
Lucknow : 8855865060
Dubai : +91 8888188885
What do I feel during the procedure?
What happens after the operation?
When can I go home?
What are my visits to the toilet going to be like?
What helps constipation fast? Or How do you cure constipation quickly?
Should I see a gastroenterologist for constipation?
When should you go to the hospital for constipation?
What do I feel during the procedure?
What happens after the operation?
Do I need to follow any specific diet before/after fistula surgery?
When can I return to my normal activities?
In how many days can I start travelling after a fistula surgery?
Does smoking affect hernia?
What are the risks / complications of a hernia surgery?
What do I feel during the procedure ?
What happens after the operation?
What do I feel during the surgery ?
When can I get back to my routine activities?
How do I ensure appropriate wound care?
What is the role of permanent hair removal in preventing recurrence?
Are varicose veins serious or life-threatening?
Can varicose veins recur following therapy?
Is laser varicose vein treatment painful?
Are varicose veins preventable?
What are lifestyle modifications to control faecal incontinence?
What is a standard treatment plan for faecal incontinence?
Is biofeedback therapy painful or unpleasant? What am I going to feel during it?
Do I need surgery to manage faecal incontinence?
Is it a bloodless procedure?
Why is it called a pain-free treatment?
How do no sutures/ stitches work in this procedure?
What are the chances of contracting HIV/HEPATITIS B infection?
Can rectal prolapse resolve by itself without being treated?
Is rectal prolapse a cancer type or does it cause cancer?
How can I tell if I have rectal prolapse or only hemorrhoids?
Is surgery the only treatment for rectal prolapse?
Is a rectal abscess identical with a haemorrhoid?
Can a rectal abscess improve by itself without treatment?
What is the duration of recovery after drainage of abscess?
Is a rectal abscess an indicator of a serious medical condition?
Biofeedback therapy ( BFT ) is an instrument-based learning process; it uses equipment to record or amplify a patient's anorectal activity and then provides feedback to the patient and therapist. The goal of anorectal BFT is to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, retrain rectal sensation, and coordinate the activity of abdominal, pelvic floor and sphincter muscles during evacuation.
Pelvic floor dyssynergia affects almost 40% patients of chronic constipation. It is an acquired ( i.e. one isn't born with it ) behavioural problem wherein the coordination between the abdominal and pelvic floor muscles to evacuate stools is disturbed. The anal and rectal area contains specialized muscles that are helpful to regulate proper passage of stools during bowel movements. Normally, when stool enters the rectum, the anal sphincter muscle tightens to prevent passage of stool at an inconvenient time. When a person pushes or bears down to have a bowel movement, the anal sphincter muscles relax. This will cause the pressures to decrease allowing evacuation of stool.
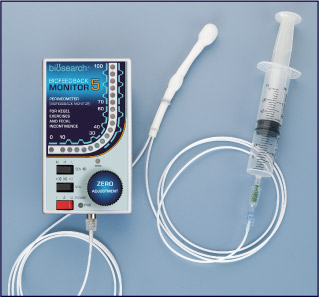
However, if the sphincter muscles tighten when pushing, this could contribute to constipation. Thus, in patients with constipation caused due to muscle dyssnergia the anal sphincter muscles do not relax appropriately when bearing down to have a bowel movement creating a functional type of obstruction. These muscles that do not relax with bearing down can be retrained with biofeedback.
As mentioned above, when stools enter the rectum, the anal sphincter muscles tighten to prevent untimely passage of stools, However, if this muscle is weak or does not contract in a timely way, incontinence ( leakage of stool ) may occur. Biofeedback techniques using anal manometry and pelvic floor physiotherapy can strengthen the sphincter muscles and improve rectal sensation. This can help treat faecal incontinence.
At Healing Hands Clinic, manometry is used to gauge pressure changes in the anorectum. The balloon and manometry probe located in the rectum and anal canal record the pressure changes during different manoeuvres. These changes are visible on the monitor for the patient and therapist to see. The therapist explains the results and guides the patient towards changes that are needed in abdominal push effort and recto-anal coordination. The purpose of training in patients with dyssynergic constipation is to create an adequate abdominal push effort that synchronizes with relaxation of the anal sphincters. In faecal incontinence, the purpose is to increase the strength of contraction of the anal sphincter.
BFT is the most effective treatment for chronic constipation due to pelvic floor dyssnergia. After completing the initial training program, periodic reinforcement sessions at 3 months, 6 months and 1 year gives a much better outcome in the long run.
schedule your consultation with our experts now.

Welcome to Healing Hands Clinic, where our expert team provides compassionate and specialized care in proctology. Our state-of-the-art facility ensures the highest standards of treatment and comfort for our patients. We prioritize your well-being and strive to make your experience as seamless and stress-free as possible. Trust Healing Hands Clinic for professional and personalized proctological care.
Copyright © Healing Hands Clinic Pvt. Ltd 2024, All rights reserved.
Designed And Developed By Innothoughts System Pvt. Ltd